K Boyce
A molecular and ecological analysis of the trematode plagiorchis elegans in the wood mouse apodemus sylvaticus from a periaquatic ecosystem in the UK
Boyce, K; Hide, G; Craig, PS; Reynolds, C; Hussain, M; Bodell, AJ; Bradshaw, H; Pickles, A; Rogan, MT
Authors
Prof Geoff Hide G.Hide@salford.ac.uk
Professor
PS Craig
C Reynolds
M Hussain
AJ Bodell
H Bradshaw
A Pickles
MT Rogan
Abstract
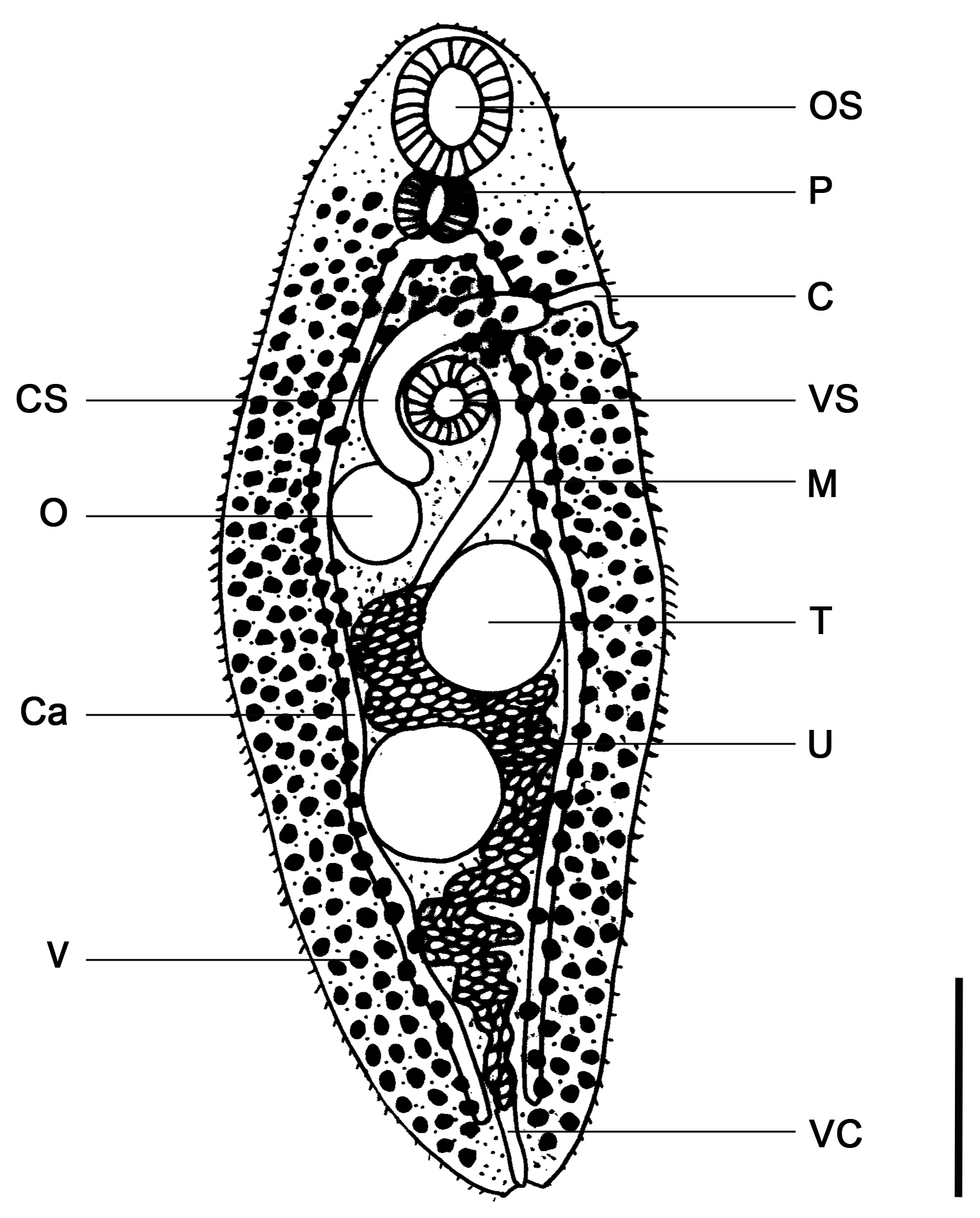
The prevalence of the digenean Plagiorchis sp. was investigated in a natural
wood mouse population (Apodemus sylvaticus) in a periaquatic environment.
Classical identification was complemented with the use of molecular
differentiation to determine prevalence and verify species identity. Use of the
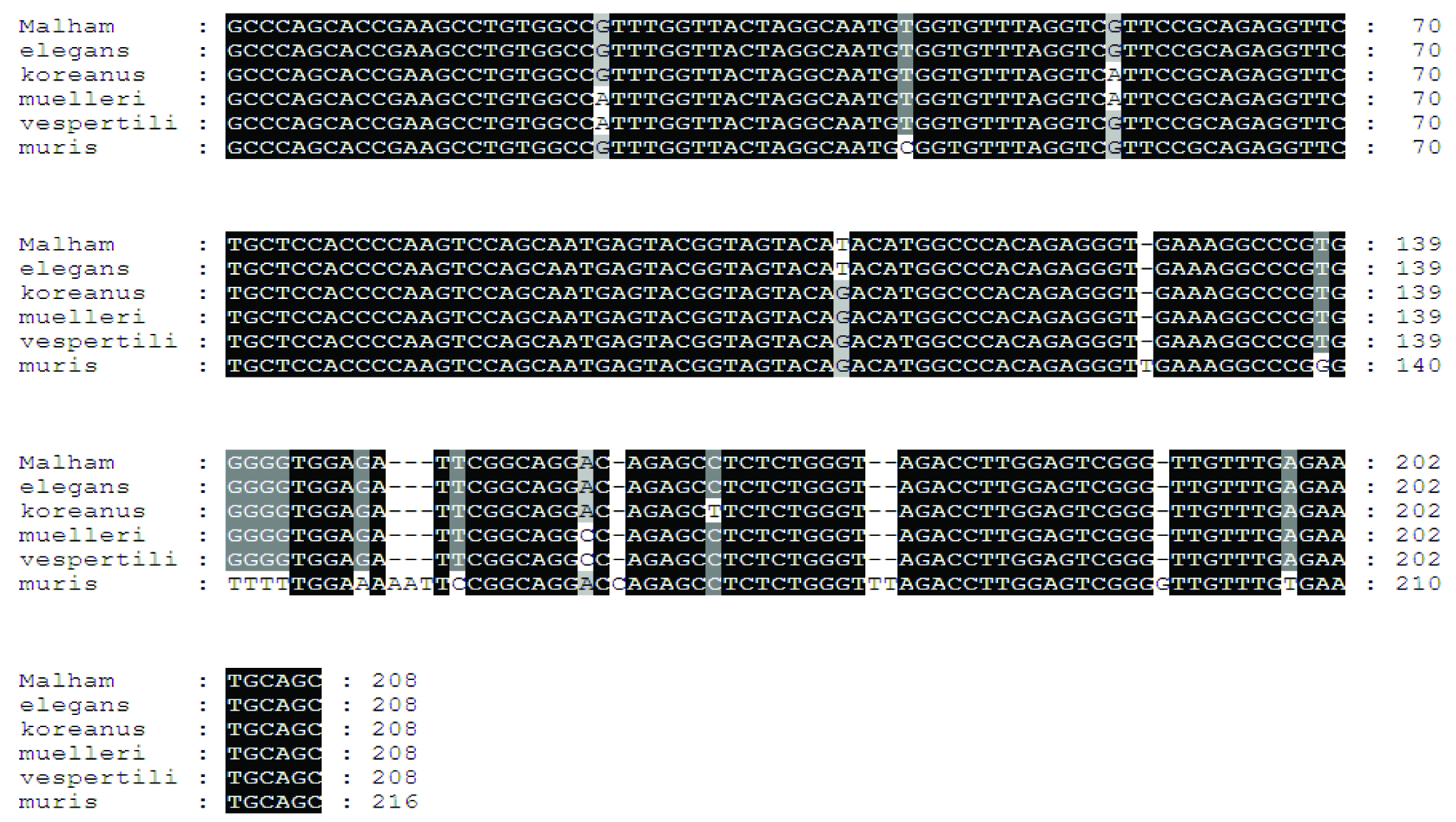
complete ITS1-5.8S rDNA-ITS2 and partial 28S rDNA gene sequences have
confirmed that the species reported at this location was Plagiorchis elegans and
not Plagiorchis muris as reported previously. This underlines the difficulties in
identification of these morphologically similar parasites. Plagiorchis elegans is
typically a gastrointestinal parasite of avian species but has also been reported
from small mammal populations. Although the occurrence of this digenean in
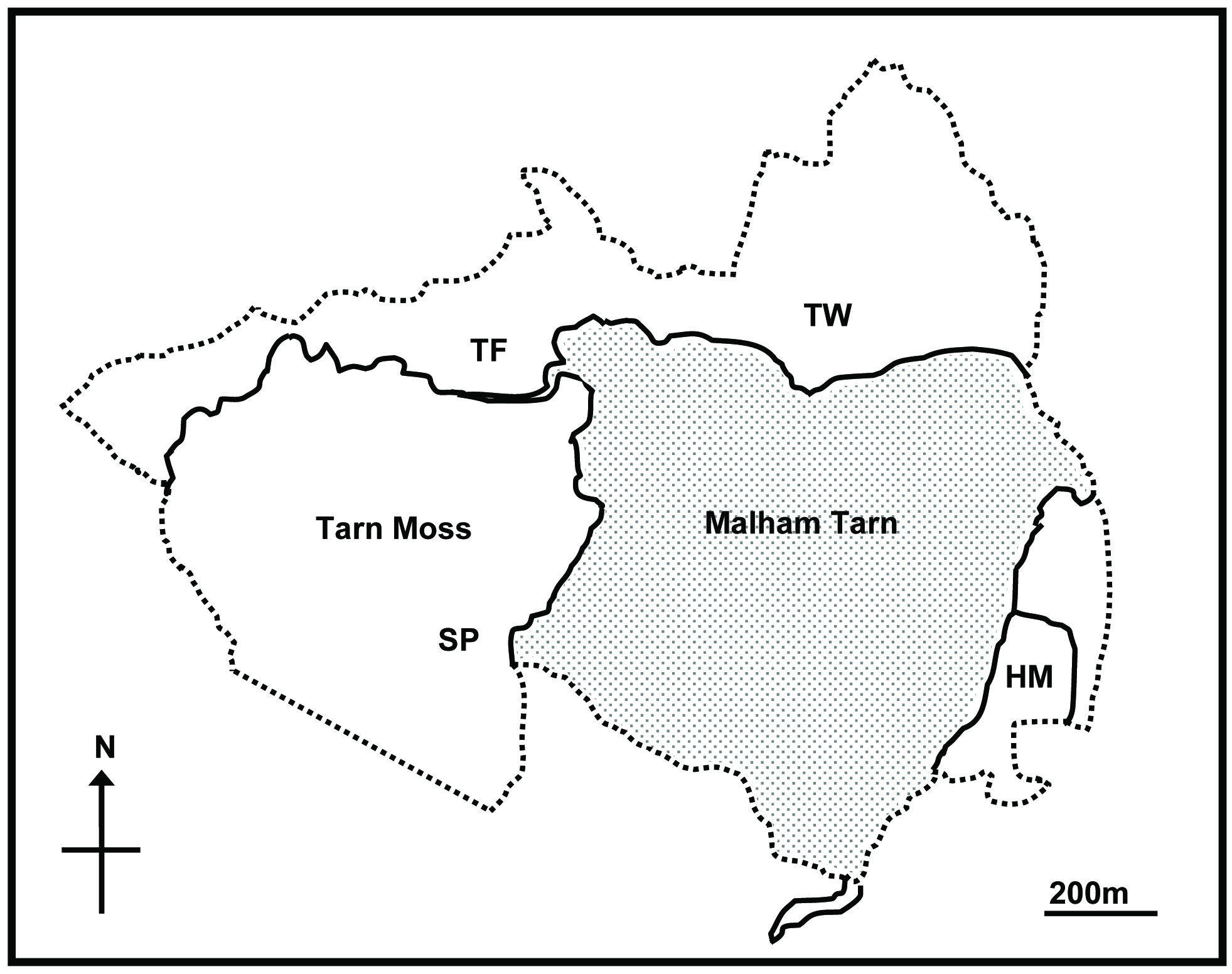
A. sylvaticus in the UK is rare, in the area immediately surrounding Malham
Tarn, Yorkshire, it had a high prevalence (23%) and a mean worm burden of
26.6 ^ 61.5. The distribution of P. elegans followed a typically overdispersed
pattern and both mouse age-group and sex were determined to be two main
factors associated with prevalence. Male mice harboured the majority of worms,
carrying 688 of 717 recovered during the study, and had a higher prevalence of
32.4% in comparison to only 8.7% in the small intestine of female mice. A higher
prevalence of 43% was also observed in adult mice compared to 14% for young
adults. No infection was observed in juvenile mice. These significant differences
are likely to be due to differences in the foraging behaviour between the sexes
and age cohorts of wood mice.
| Journal Article Type | Article |
|---|---|
| Publication Date | Apr 19, 2013 |
| Deposit Date | Feb 10, 2015 |
| Publicly Available Date | Apr 5, 2016 |
| Journal | Journal of Helminthology |
| Print ISSN | 0022-149X |
| Electronic ISSN | 1475-2697 |
| Publisher | Cambridge University Press (CUP) |
| Peer Reviewed | Peer Reviewed |
| Volume | 88 |
| Issue | 03 |
| Pages | 310-320 |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X13000199 |
| Publisher URL | http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X13000199 |
| Related Public URLs | http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=9314061&fileId=S0022149X13000199 |
| Additional Information | Funders : Nuffield Foundation;British Society for Parasitology |
Files
Final_Plagiorchis_Draft050912v2_Submitted.pdf
(753 Kb)
PDF
Figure_3_DNA_sequence_data.jpg
(3 Mb)
Image
Figure_2_Plagiorchis_image.jpg
(843 Kb)
Image
Figure_1_Malham_Tarn_map.jpg
(1.9 Mb)
Image
You might also like
Downloadable Citations
About USIR
Administrator e-mail: library-research@salford.ac.uk
This application uses the following open-source libraries:
SheetJS Community Edition
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
PDF.js
Apache License Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/)
Font Awesome
SIL OFL 1.1 (http://scripts.sil.org/OFL)
MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html)
CC BY 3.0 ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
Powered by Worktribe © 2025
Advanced Search